This comprehensive guide will walk you through integrating Google Cloud Storage (GCS) with Django for file operations, including project structure, configuration, and implementation.
Table of Contents
- Project Setup
- Google Cloud Storage Configuration
- Django Model Setup
- Views Implementation
- Templates
- URLs Configuration
- Final Project Structure
- Testing
- Deployment Considerations
Project Setup
First, let's create a new Django project and app:
# Create project directory
mkdir django-gcs-project
cd django-gcs-project
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
# Install required packages
pip install django google-cloud-storage django-storages[google] python-dotenvGoogle Cloud Storage Configuration
1. Set up a Google Cloud Project:
- Go to Google Cloud Console
- Create a new project or select an existing one
- Enable "Google Cloud Storage API"
2. Create a Service Account:
- Navigate to "IAM & Admin" > "Service Accounts"
- Create a new service account with "Storage Admin" role
- Generate a JSON key and download it
3. Create a Storage Bucket:
- Go to "Cloud Storage" > "Buckets"
- Create a new bucket with your preferred settings
4. Environment Configuration:
Create a .env file in your project root:
GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS=path/to/your/service-account-key.json
GS_BUCKET_NAME=your-bucket-name
GS_PROJECT_ID=your-project-id5. Update Django Settings:
In your settings.py:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
# Google Cloud Storage settings
DEFAULT_FILE_STORAGE = 'storages.backends.gcloud.GoogleCloudStorage'
GS_BUCKET_NAME = os.getenv('GS_BUCKET_NAME')
GS_PROJECT_ID = os.getenv('GS_PROJECT_ID')
GS_FILE_OVERWRITE = False # Set to True if you want to overwrite files with same names
# For serving files publicly (optional)
GS_DEFAULT_ACL = 'publicRead'Django Model Setup
Create a model to track uploaded files in your app's models.py:
from django.db import models
from django.utils import timezone
from django.urls import reverse
class StorageFile(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=255)
file = models.FileField(upload_to='uploads/')
uploaded_at = models.DateTimeField(default=timezone.now)
size = models.PositiveIntegerField(default=0)
content_type = models.CharField(max_length=100, blank=True)
class Meta:
ordering = ['-uploaded_at']
def __str__(self):
return self.name
def get_absolute_url(self):
return reverse('file_detail', kwargs={'pk': self.pk})
def save(self, *args, **kwargs):
# Set file size and content type before saving
if self.file:
self.size = self.file.size
self.content_type = self.file.file.content_type
super().save(*args, **kwargs)
def delete(self, *args, **kwargs):
# Delete file from storage when model is deleted
self.file.delete()
super().delete(*args, **kwargs)Views Implementation
Create views for file operations in your app's views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, get_object_or_404
from django.views.generic import ListView, DetailView
from django.views.generic.edit import CreateView, DeleteView
from django.urls import reverse_lazy
from django.contrib import messages
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect, FileResponse
from .models import StorageFile
from .forms import FileUploadForm
from google.cloud import storage
import os
class FileListView(ListView):
model = StorageFile
template_name = 'storage/file_list.html'
context_object_name = 'files'
paginate_by = 10
class FileDetailView(DetailView):
model = StorageFile
template_name = 'storage/file_detail.html'
context_object_name = 'file'
class FileUploadView(CreateView):
model = StorageFile
form_class = FileUploadForm
template_name = 'storage/file_upload.html'
success_url = reverse_lazy('file_list')
def form_valid(self, form):
response = super().form_valid(form)
messages.success(self.request, f'File "{self.object.name}" uploaded successfully!')
return response
class FileDeleteView(DeleteView):
model = StorageFile
template_name = 'storage/file_confirm_delete.html'
success_url = reverse_lazy('file_list')
def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
messages.success(request, f'File "{self.get_object().name}" deleted successfully!')
return super().delete(request, *args, **kwargs)
def download_file(request, pk):
file_obj = get_object_or_404(StorageFile, pk=pk)
# For public files, redirect to the direct URL
if os.getenv('GS_DEFAULT_ACL') == 'publicRead':
return HttpResponseRedirect(file_obj.file.url)
# For private files, use the Google Cloud Storage client
client = storage.Client()
bucket = client.get_bucket(os.getenv('GS_BUCKET_NAME'))
blob = bucket.blob(file_obj.file.name)
# Create a streaming response
response = FileResponse(blob.open('rb'), content_type=file_obj.content_type)
response['Content-Disposition'] = f'attachment; filename="{file_obj.name}"'
return responseForms
Create a form in forms.py for file uploads:
from django import forms
from .models import StorageFile
class FileUploadForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = StorageFile
fields = ['name', 'file']
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.fields['name'].widget.attrs.update({'class': 'form-control'})
self.fields['file'].widget.attrs.update({'class': 'form-control'})Templates
Create the following templates in your app's templates/storage/ directory:
1. file_list.html:
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block content %}
<div class="container mt-4">
<h2>File List</h2>
<a href="{% url 'file_upload' %}" class="btn btn-primary mb-3">Upload File</a>
{% if messages %}
{% for message in messages %}
<div class="alert alert-{{ message.tags }}">{{ message }}</div>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Uploaded</th>
<th>Size</th>
<th>Type</th>
<th>Actions</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for file in files %}
<tr>
<td>{{ file.name }}</td>
<td>{{ file.uploaded_at|date:"Y-m-d H:i" }}</td>
<td>{{ file.size|filesizeformat }}</td>
<td>{{ file.content_type }}</td>
<td>
<a href="{% url 'file_detail' file.pk %}" class="btn btn-sm btn-info">View</a>
<a href="{% url 'file_download' file.pk %}" class="btn btn-sm btn-success">Download</a>
<a href="{% url 'file_delete' file.pk %}" class="btn btn-sm btn-danger">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
{% empty %}
<tr>
<td colspan="5">No files uploaded yet.</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
{% if is_paginated %}
<div class="pagination">
<span class="step-links">
{% if page_obj.has_previous %}
<a href="?page=1">« first</a>
<a href="?page={{ page_obj.previous_page_number }}">previous</a>
{% endif %}
<span class="current">
Page {{ page_obj.number }} of {{ page_obj.paginator.num_pages }}.
</span>
{% if page_obj.has_next %}
<a href="?page={{ page_obj.next_page_number }}">next</a>
<a href="?page={{ page_obj.paginator.num_pages }}">last »</a>
{% endif %}
</span>
</div>
{% endif %}
</div>
{% endblock %}2. file_upload.html:
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block content %}
<div class="container mt-4">
<h2>Upload File</h2>
<form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
{{ form.name.label_tag }}
{{ form.name }}
</div>
<div class="form-group">
{{ form.file.label_tag }}
{{ form.file }}
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Upload</button>
<a href="{% url 'file_list' %}" class="btn btn-secondary">Cancel</a>
</form>
</div>
{% endblock %}4. file_detail.html:
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block content %}
<div class="container mt-4">
<h2>File Details: {{ file.name }}</h2>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">{{ file.name }}</h5>
<p class="card-text">
<strong>Uploaded:</strong> {{ file.uploaded_at|date:"Y-m-d H:i" }}<br>
<strong>Size:</strong> {{ file.size|filesizeformat }}<br>
<strong>Type:</strong> {{ file.content_type }}<br>
<strong>URL:</strong> <a href="{{ file.file.url }}" target="_blank">{{ file.file.url }}</a>
</p>
<a href="{% url 'file_download' file.pk %}" class="btn btn-primary">Download</a>
<a href="{% url 'file_delete' file.pk %}" class="btn btn-danger">Delete</a>
<a href="{% url 'file_list' %}" class="btn btn-secondary">Back to List</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}5. file_confirm_delete.html:
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block content %}
<div class="container mt-4">
<h2>Confirm Delete</h2>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">Are you sure you want to delete "{{ object.name }}"?</h5>
<p class="card-text">This action cannot be undone.</p>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-danger">Yes, delete</button>
<a href="{% url 'file_detail' object.pk %}" class="btn btn-secondary">Cancel</a>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}URLs Configuration
In your app's urls.py:
from django.urls import path
from .views import (
FileListView, FileDetailView,
FileUploadView, FileDeleteView,
download_file
)
urlpatterns = [
path('', FileListView.as_view(), name='file_list'),
path('upload/', FileUploadView.as_view(), name='file_upload'),
path('<int:pk>/', FileDetailView.as_view(), name='file_detail'),
path('<int:pk>/download/', download_file, name='file_download'),
path('<int:pk>/delete/', FileDeleteView.as_view(), name='file_delete'),
]Include this in your project's main urls.py:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('files/', include('your_app_name.urls')),
]Final Project Structure
Here's the complete project structure:
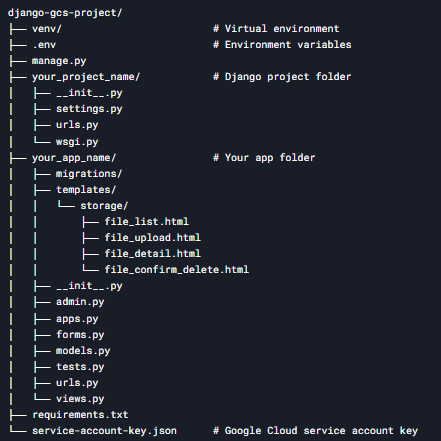
Testing
- Run the development server:bashCopypython manage.py makemigrations python manage.py migrate python manage.py createsuperuser python manage.py runserver
- Test the following functionality:
- File upload (should appear in your GCS bucket)
- File listing (should show all uploaded files)
- File download (should download the file)
- File deletion (should remove from both database and GCS)
Deployment Considerations
- Security:
- Never commit your service account key to version control
- Use environment variables in production
- Consider setting more restrictive permissions for your service account
- Performance:
- For large files, consider using signed URLs for downloads
- Implement client-side uploads directly to GCS for very large files
- Cost Optimization:
- Set up lifecycle rules in GCS to automatically delete old files
- Consider using different storage classes for different types of files
- Additional Features:
- Add file preview functionality for images and PDFs
- Implement file sharing with expiration dates
- Add folder/tag organization for files
This complete implementation provides a solid foundation for file management with Django and Google Cloud Storage, covering all CRUD operations with proper error handling and user feedback.