Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Project Setup
- Configuring Multiple DataSources
- Liquibase Configuration
- Database Change Management
- CI/CD Integration
- Best Practices
- Troubleshooting
Introduction
This guide provides a comprehensive approach to managing database migrations for multiple databases (MySQL and PostgreSQL) in a Spring Boot application using Liquibase, including CI/CD pipeline integration.
Prerequisites
- Java 11+
- Spring Boot 2.7+
- Maven/Gradle
- MySQL 8.0+
- PostgreSQL 13+
- Liquibase 4.0+
- Docker (for CI/CD examples)
- GitHub/GitLab account (for CI/CD examples)
Project Setup
1. Add Dependencies
Maven (pom.xml):
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Data JPA -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Liquibase -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.liquibase</groupId>
<artifactId>liquibase-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL Connector -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- PostgreSQL Connector -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- For property resolution -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Configuring Multiple DataSources
1. Application Properties
application.yml:
spring:
datasource:
mysql:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true
username: root
password: mysqlpass
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
postgres:
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydb
username: postgres
password: postgrespass
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
liquibase:
mysql:
change-log: classpath:db/changelog/mysql/master.xml
postgres:
change-log: classpath:db/changelog/postgres/master.xml2. DataSource Configuration Classes
MySQL Configuration:
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(
basePackages = "com.example.repository.mysql",
entityManagerFactoryRef = "mysqlEntityManagerFactory",
transactionManagerRef = "mysqlTransactionManager"
)
public class MySqlDataSourceConfig {
@Primary
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.mysql")
public DataSource mysqlDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Primary
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean mysqlEntityManagerFactory(
EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder
.dataSource(mysqlDataSource())
.packages("com.example.model.mysql")
.persistenceUnit("mysql")
.build();
}
@Primary
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager mysqlTransactionManager(
@Qualifier("mysqlEntityManagerFactory") EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(entityManagerFactory);
}
}PostgreSQL Configuration:
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(
basePackages = "com.example.repository.postgres",
entityManagerFactoryRef = "postgresEntityManagerFactory",
transactionManagerRef = "postgresTransactionManager"
)
public class PostgresDataSourceConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.postgres")
public DataSource postgresDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean postgresEntityManagerFactory(
EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder
.dataSource(postgresDataSource())
.packages("com.example.model.postgres")
.persistenceUnit("postgres")
.build();
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager postgresTransactionManager(
@Qualifier("postgresEntityManagerFactory") EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(entityManagerFactory);
}
}Liquibase Configuration
1. Liquibase Beans Configuration
@Configuration
public class LiquibaseConfig {
@Bean
@DependsOn("mysqlDataSource")
public SpringLiquibase mysqlLiquibase(@Qualifier("mysqlDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
SpringLiquibase liquibase = new SpringLiquibase();
liquibase.setDataSource(dataSource);
liquibase.setChangeLog("classpath:db/changelog/mysql/master.xml");
liquibase.setContexts("development, production");
liquibase.setShouldRun(true);
return liquibase;
}
@Bean
@DependsOn("postgresDataSource")
public SpringLiquibase postgresLiquibase(@Qualifier("postgresDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
SpringLiquibase liquibase = new SpringLiquibase();
liquibase.setDataSource(dataSource);
liquibase.setChangeLog("classpath:db/changelog/postgres/master.xml");
liquibase.setContexts("development, production");
liquibase.setShouldRun(true);
return liquibase;
}
}2. Directory Structure
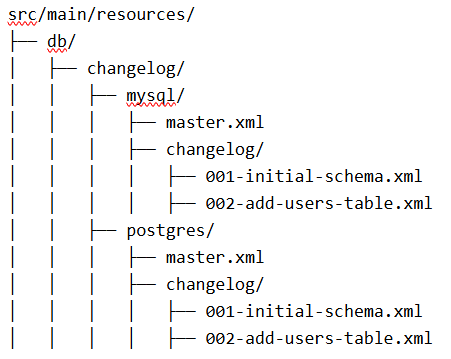
3. Master ChangeLog Files
MySQL master.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<databaseChangeLog
xmlns="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog
http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-4.1.xsd">
<includeAll path="db/changelog/mysql/changelog/" relativeToChangelogFile="true"/>
</databaseChangeLog>PostgreSQL master.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<databaseChangeLog
xmlns="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog
http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-4.1.xsd">
<includeAll path="db/changelog/postgres/changelog/" relativeToChangelogFile="true"/>
</databaseChangeLog>4. Example ChangeSet Files
MySQL 001-initial-schema.xml:
<databaseChangeLog
xmlns="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog
http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-4.1.xsd">
<changeSet id="1" author="dev">
<createTable tableName="user">
<column name="id" type="BIGINT" autoIncrement="true">
<constraints primaryKey="true" nullable="false"/>
</column>
<column name="username" type="VARCHAR(50)">
<constraints nullable="false" unique="true"/>
</column>
<column name="password" type="VARCHAR(100)">
<constraints nullable="false"/>
</column>
<column name="email" type="VARCHAR(100)">
<constraints nullable="false" unique="true"/>
</column>
<column name="created_at" type="DATETIME" defaultValueComputed="CURRENT_TIMESTAMP"/>
</createTable>
</changeSet>
</databaseChangeLog>PostgreSQL 001-initial-schema.xml:
<databaseChangeLog
xmlns="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog
http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-4.1.xsd">
<changeSet id="1" author="dev">
<createTable tableName="user">
<column name="id" type="BIGSERIAL">
<constraints primaryKey="true" nullable="false"/>
</column>
<column name="username" type="VARCHAR(50)">
<constraints nullable="false" unique="true"/>
</column>
<column name="password" type="VARCHAR(100)">
<constraints nullable="false"/>
</column>
<column name="email" type="VARCHAR(100)">
<constraints nullable="false" unique="true"/>
</column>
<column name="created_at" type="TIMESTAMP" defaultValueComputed="CURRENT_TIMESTAMP"/>
</createTable>
</changeSet>
</databaseChangeLog>Database Change Management
1. Generating ChangeSets
Use Liquibase CLI or Maven plugin to generate changesets:
# For MySQL
mvn liquibase:diff \
-Dliquibase.diffChangeLogFile=src/main/resources/db/changelog/mysql/changelog/003-new-changes.xml \
-Dliquibase.referenceUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/reference_db \
-Dliquibase.referenceUsername=root \
-Dliquibase.referencePassword=mysqlpass \
-Dliquibase.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb \
-Dliquibase.username=root \
-Dliquibase.password=mysqlpass
# For PostgreSQL
mvn liquibase:diff \
-Dliquibase.diffChangeLogFile=src/main/resources/db/changelog/postgres/changelog/003-new-changes.xml \
-Dliquibase.referenceUrl=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/reference_db \
-Dliquibase.referenceUsername=postgres \
-Dliquibase.referencePassword=postgrespass \
-Dliquibase.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydb \
-Dliquibase.username=postgres \
-Dliquibase.password=postgrespass2. Database-Specific Changes
Use the dbms attribute to specify database-specific changes:
<changeSet id="2" author="dev">
<addColumn tableName="user">
<column name="status" type="VARCHAR(20)" defaultValue="ACTIVE">
<constraints nullable="false"/>
</column>
</addColumn>
<!-- MySQL specific index -->
<createIndex indexName="idx_user_status" tableName="user" dbms="mysql">
<column name="status"/>
</createIndex>
<!-- PostgreSQL specific index -->
<createIndex indexName="idx_user_status" tableName="user" dbms="postgresql">
<column name="status"/>
</createIndex>
</changeSet>CI/CD Integration
1. GitHub Actions Workflow
.github/workflows/ci.yml:
name: CI Pipeline
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
build-and-test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
services:
mysql:
image: mysql:8.0
env:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: mysqlpass
MYSQL_DATABASE: mydb
ports:
- 3306:3306
options: --health-cmd="mysqladmin ping" --health-interval=10s --health-timeout=5s --health-retries=3
postgres:
image: postgres:13
env:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgrespass
POSTGRES_DB: mydb
ports:
- 5432:5432
options: --health-cmd="pg_isready" --health-interval=10s --health-timeout=5s --health-retries=3
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up JDK 11
uses: actions/setup-java@v2
with:
java-version: '11'
distribution: 'adopt'
- name: Build with Maven
run: mvn -B package --file pom.xml
- name: Run Liquibase migrations for MySQL
run: |
mvn liquibase:update \
-Dliquibase.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb \
-Dliquibase.username=root \
-Dliquibase.password=mysqlpass \
-Dliquibase.changeLogFile=src/main/resources/db/changelog/mysql/master.xml
- name: Run Liquibase migrations for PostgreSQL
run: |
mvn liquibase:update \
-Dliquibase.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydb \
-Dliquibase.username=postgres \
-Dliquibase.password=postgrespass \
-Dliquibase.changeLogFile=src/main/resources/db/changelog/postgres/master.xml
- name: Run tests
run: mvn test2. Docker Deployment
Dockerfile:
FROM openjdk:11-jre-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY target/your-application.jar /app/app.jar
# Install wait-for-it.sh for container dependencies
ADD https://github.com/vishnubob/wait-for-it/raw/master/wait-for-it.sh /wait-for-it.sh
RUN chmod +x /wait-for-it.sh
CMD ["sh", "-c", "./wait-for-it.sh mysql:3306 --timeout=30 -- ./wait-for-it.sh postgres:5432 --timeout=30 -- java -jar app.jar"]docker-compose.yml:
version: '3.8'
services:
app:
build: .
ports:
- "8080:8080"
depends_on:
- mysql
- postgres
environment:
SPRING_DATASOURCE_MYSQL_URL: jdbc:mysql://mysql:3306/mydb
SPRING_DATASOURCE_MYSQL_USERNAME: root
SPRING_DATASOURCE_MYSQL_PASSWORD: mysqlpass
SPRING_DATASOURCE_POSTGRES_URL: jdbc:postgresql://postgres:5432/mydb
SPRING_DATASOURCE_POSTGRES_USERNAME: postgres
SPRING_DATASOURCE_POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgrespass
mysql:
image: mysql:8.0
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: mysqlpass
MYSQL_DATABASE: mydb
ports:
- "3306:3306"
volumes:
- mysql_data:/var/lib/mysql
postgres:
image: postgres:13
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgrespass
POSTGRES_DB: mydb
ports:
- "5432:5432"
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
mysql_data:
postgres_data:Best Practices
- Database-Specific Changesets:
- Keep separate changelog directories for each database
- Use
dbmsattribute for database-specific changes
- ChangeSet Management:
- Each changeset should be atomic and idempotent
- Include rollback instructions for each changeset
- Use meaningful IDs and comments
- Version Control:
- Store all changelog files in version control
- Use a consistent naming convention (e.g.,
001-...,002-...)
- CI/CD:
- Run migrations as part of your deployment pipeline
- Test migrations in a staging environment before production
- Consider using Liquibase Pro for more advanced features in production
- Environment Management:
- Use contexts to control which changesets run in which environments
- Consider using Liquibase labels for more complex environment targeting
Troubleshooting
- Connection Issues:
- Verify database URLs, usernames, and passwords
- Check network connectivity between application and databases
- Ensure databases are running and accessible
- Migration Failures:
- Check Liquibase logs for specific error messages
- Verify the changelog files are correctly formatted
- Ensure the database user has sufficient privileges
- Multiple DataSource Conflicts:
- Verify
@Primaryannotations are correctly placed - Check package scanning configurations for JPA entities
- Ensure transaction managers are properly scoped
- Verify
- Performance Issues:
- For large databases, consider using
liquibase.updateCountto run migrations in batches - Review indexes and constraints for performance impact
- For large databases, consider using
- Lock Issues:
- If migrations fail, Liquibase may leave a lock in the database
- Manually remove locks from the
DATABASECHANGELOGLOCKtable if needed